When we think about wearables, popular consumer examples like the FitBit and Apple Watch come to mind. But this is a lot like comparing personal and professional computer usage.
While a computer is a great tool for communicating with friends and browsing the web, its real potential is unlocked in the business world, whether that’s analyzing data, collaborating with global partners and leading industry innovation.
The same is also true for wearables. While we’ve already seen interesting technology solutions in healthcare, Industry & Manufacturing is where they will truly break new ground offering a myriad of benefits to companies and people working in:
- Oil & gas
- Utilities
- Mining
- Manufacturing
- Logistics
- Transportation
- Construction industries.
Join us as we explore the growing role of wearable tech in heavy industry and preview a more efficient, safe and cost-effective way of getting things built, shipped and delivered.
Industrial wearable technology in action
Wearable technology refers to a broad array of gadgets, devices, sensors and more. In particular, when we discuss the topic, we're describing tools like:
- Augmented reality (AR) glasses
- Exoskeletons
- Biometric sensors
- Hearables
While these technologies all vastly differ, they do share something in common. All of them empower industry workers, helping them perform their jobs better through different enhancements.
More importantly, they are vital for health and safety in the workplace, and this has numerous benefits for both individual workers and corporations. The result is reduced costs, lowered unplanned downtime, better injury prevention, and better risk assessment and mitigation tools.
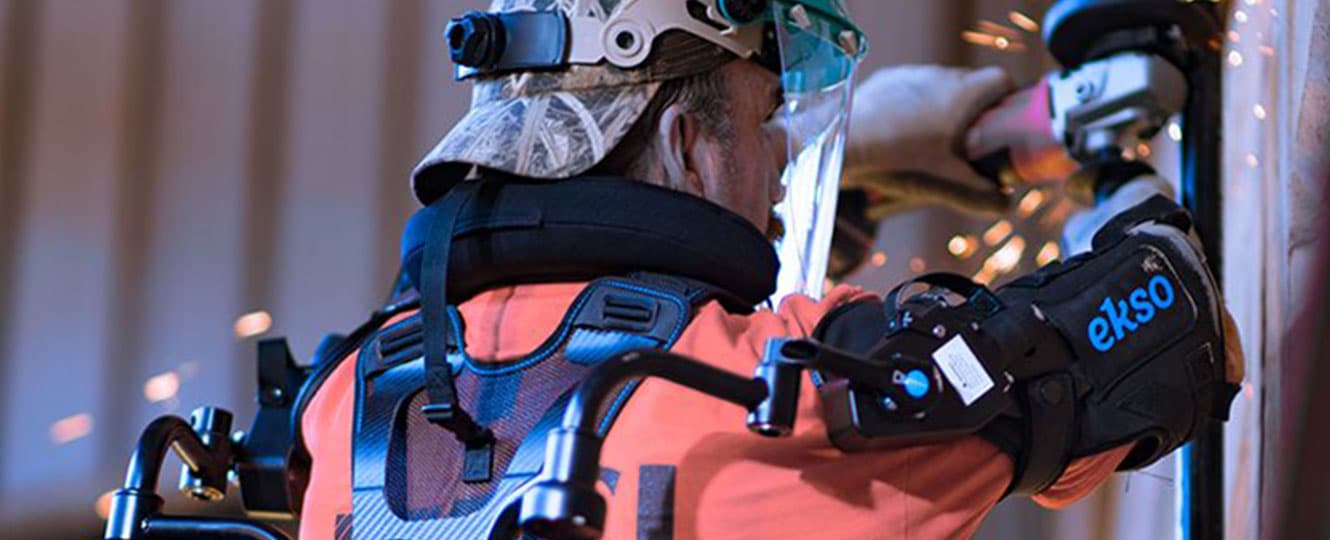
Products like Sarcos Robotics Guardian XO gives us a preview of what an augmented industrial future will look like. The smart exoskeleton combines human intelligence with mechanical strength amplifying a person’s power by up to 20 times! But it’s not just about strength but reducing strain and industry on workers, especially those working in hazardous environments.
Here are three ways wearable technologies are transforming industry and manufacturing.
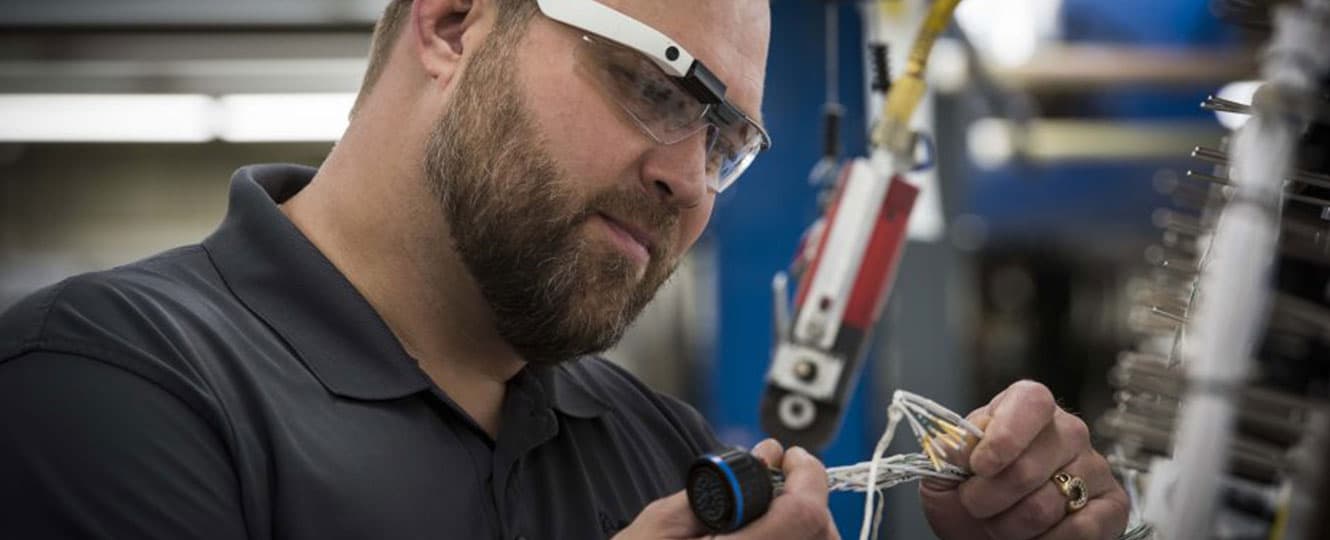

1. Human error prevention
We all make mistakes. That’s part of being human. But great businesses know how to account for error and minimize the impact. According to IBM, the cost of error varies immensely across industries, but it can add up to millions of dollars in lost revenue, productivity, and missed opportunities.
This is one area where AR glasses have already seen widespread industrial usage at leading firms like Boeing, GE and DHL.
For example, Boeing is using AR glasses powered by Skylight to visually guide technicians through the complex process of wiring hundreds of planes a year. The result has been radically improved worker productivity while decreasing production time by 25%.
Other applications have been equally effective in tracking worker stress and fatigue. Fatigue Science’s Readi is an enterprise suite of tools. Readi integrates with existing wearable tech like FitBits along with their own proprietary Readiband devices. The software analyzes data to predict the impact of sleep on key performance factors, including:
- Reaction time
- Cognitive effectiveness
- Fatigue state
- Alertness
These data points can then be used at the individual and management level to prevent errors through something as simple as knowing when to take a break to a longer-term structural plan.
Another technology we have our eye on is GuardHat. This smart hard-hat can measure workers’ activity levels, reduce error, and create an additional safety layer for those in hazardous environments. Best of all, it syncs with Industrial IoT networks as a part of larger tech workplace.
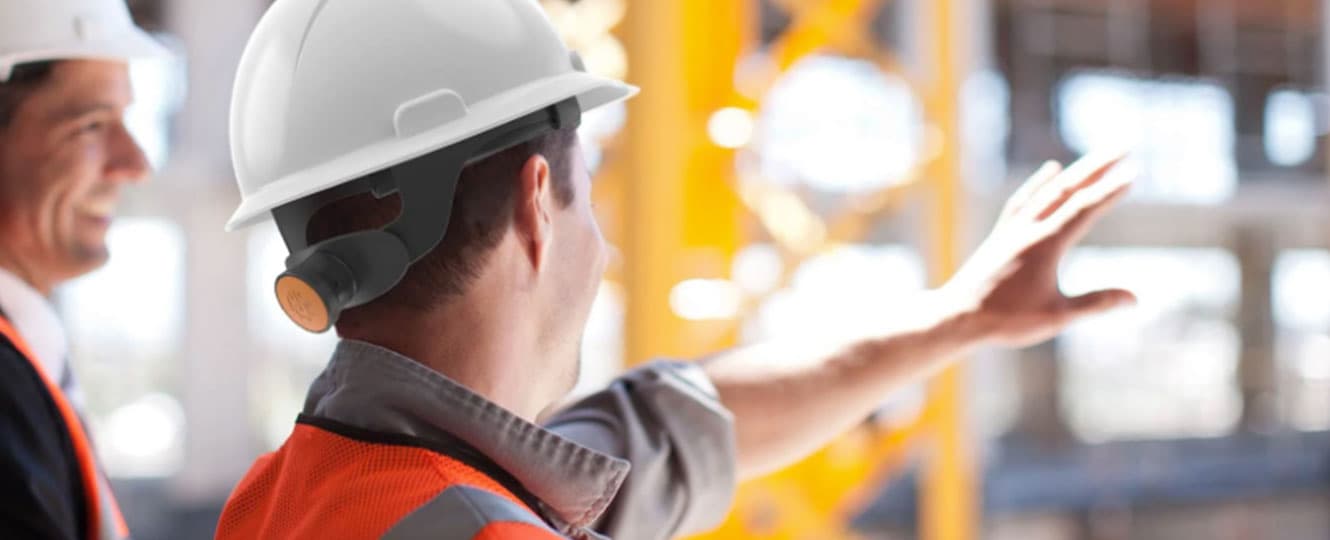

2. Enhancing safety and physical endurance
According to the 2020 Liberty Mutual Workplace Safety Index, workplace injuries cost businesses $59 billion annually.
Leading causes of injury include:
- Handling objects like lifting heavy boxes: $14B
- Falls on the same level: $10.84B
- Bing hit by objects: $6.12B
- Awkward postures: $4.69B
- Repetitive motions: $2.05B
You can see where we’re going with this. All of these problems can be solved or at least reduced through wearable technology. This is again an area where we are excited about exoskeletons like Ekso, which enhance strength and reduce fatigue and strain.
But reducing injury and improving performance doesn’t just come from flashy applications of technology like exoskeletons. Even small fatigue sensors like Readiband are powerful tools, and they are much easier to sync into daily routines than some of the grander applications of technology.
Across industries, one of our passions here at Star is the power of virtual and voice coaches. The same tools used for athletes and patients can also be harnessed in the workplace to provide coach and assistance where people need it most.

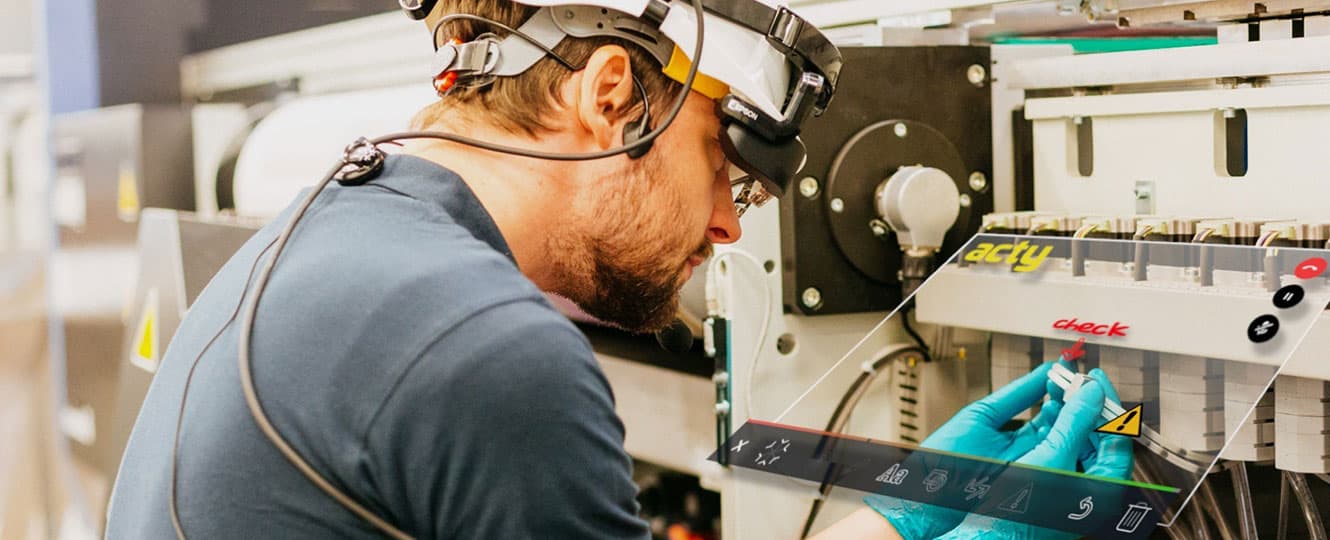
3. On-the-job skills training and enhancement
In the third quarter of 2020, about 28.6 million Baby Boomers reported that they were out of the labor force due to retirement. With 10,000 Americans turning 65 each day, this pace will only continue to accelerate as the country faces a critical skills shortage crisis.
On average, a new machine operator requires 18 days of training, while 72% of manufacturers still rely on traditional shadowing or on-the-floor training methodologies. This is all a heavy investment for companies with no guarantee that any of this training will immediately pay off as it still takes workers time to adjust to their new roles once the hand-off occurs.
“Remote expert” solutions are an excellent solution to this problem. With them, more senior technicians can guide newer staff from a central control room. From here, the field technician wears a pair of AR glasses enabling the “expert” in control to see, hear and advise accordingly.
These AR software providers have even begun experimenting with graphical overlays to transfer information into the technician’s field of vision via the glasses similar to Boeing’s project described above.
The technology is still in its infancy, but it’s easy to see the types of positive outcomes it can have. It can allow senior technicians who may be suffering from age-related mobility issues to safely lend their expertise and guidance to the next generation of workers. They’ll even be able to stay on the jobs longer if they desire to remain active past the retirement age.

How to start harnessing industrial wearable technology
At Star, we think data-first. The wearables are the conduit through which the data flows. With data science, companies can drive new strategies to promote safety and efficiency.
On the whole, Heavy Industry firms can, by culture, be change-resistant. But we live in an increasingly digital transformed world. With the ongoing effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, it’s imperative to start embracing these technology solutions now.
To help you unlock the potential of enterprise wearables, we outline three key principles to drive workforce adoption:
1. Put health and safety first
This is now more important than ever. It’s your responsibility to ensure your employee’s safety. Let alone; it’s an issue of optics. It only takes one incident of management carelessness to go viral and tarnish your reputation.
Many factory workers and technicians will not appreciate the eye of something keeping an eye on them at all times. Help them understand that these tools aren’t “watching over” but “watching out” for them. This means bringing them in on these conversations and respecting their privacy as much as possible. This will empower them to share this vital operational data with you willingly.
2. Make sure your tech solutions are relevant
No matter who your users are, always be relevant to them. Technology should always be a burden and not a benefit.
As you build and integrate wearable tech, keep these ideas in mind:
- A user-friendly and intuitive interface
- Easy integration into current workflows
- It makes things their job and isn’t just a flashy piece of tech
- It provides data streams and insights to inform decision making
3. Create familiar and joyful experiences
Just because something is used in Heavy Industry doesn’t mean it shouldn’t look nice and convey a warm atmosphere. Too often, there is an association with heavy industry with ruggedness and durability.
While important, don’t underestimate how much a delightful experience can drive long term engagement. This is why consumer apps and devices have been such a success.
Recognize that your workforce comprises consumers. Underneath their protective overalls are smartphones that navigate social media, FinTech, and other intuitive and delightful user experiences.
Enterprise applications and products that similarly feel and behave like their consumer counterparts can drive this adoption by offering that familiarity because familiarity isn’t just comforting but also easier to use and integrate.
Lead heavy industry innovation
Heavy industry is transforming quickly. Like other areas, it faces significant challenges, including health and safety risks, worker shortages, and ever-evolving demand for new skills.
At Star, we help our partners ideate, co-create and launch groundbreaking innovation for their stakeholders. Whether it’s cloud-based augmented workflows for disruptors like Fetch Robotics, knowledge bases, or other tools, we can help future-proof your business in these times of unprecedented change.
Reach out to our Industry & Manufacturing experts now to learn more about what we can do for you.